Dirt, Demolition & Definitions: The Ultimate Construction Glossary

At Triad Technologies, we understand that a successful construction site relies on having the right tools and resources at your fingertips. That's why we go beyond just providing durable, high-quality equipment from trusted brands. We're committed to being your one-stop-shop for everything you need to get the job done. In addition to our extensive inventory, we offer valuable resources like this glossary of construction terms. This comprehensive list will help ensure your crew can confidently identify and reference the essential equipment and tools needed throughout your next project.
Glossary of Terms
Angling dozer: A bulldozer with a blade that can be rotated to the side to pile dirt to the left or right.
Articulating boom platform: A lift with two or more connected arms (booms) that can bend, allowing it to reach over or around obstacles.
Axis of rotation: The imaginary vertical axis around which the upper part of a crane turns.
Backhoe-pullshovel: A machine with a digging arm and bucket that scoops dirt towards itself.
Basket derrick: A derrick (lifting device) hung by cables from a higher structure. By adjusting the cable lengths, the derrick can be moved vertically.
Blade: The flat metal part of an excavator that pushes and levels dirt, but doesn't scoop it up.
Boom: A long arm on a machine that pivots up and down from the base. The bottom of the boom is attached to a frame, mast, or post, and the top is held up by chains, ropes, or rods that connect it back to the same frame or mast. On a revolving shovel (a type of excavator), the boom is a beam hinged at the front of the machine. It's supported by cables and holds the digging bucket at the other end.
Booster pump: An extra pump that increases water pressure in a pipe in the discharge line of another pump.
Bucket loader: A tractor with a front-mounted bucket for scooping and loading materials. This may include shovel dozers, tractor loaders, and chain bucket loaders.
Bulldozer: A tractor with a large blade in front for pushing dirt.
Cat: Short for "caterpillar," which can refer to a crawler tractor or any machine made by the Caterpillar Tractor Company.
Chain bucket loader: A loader that uses a series of buckets on a chain to scoop up soil and lift it to a higher dump point.
Cherry picker: A small truck-mounted derrick with an arm and winch, used for lifting people or materials.
Chicago boom derrick: A derrick with a boom that is secured to a fixed upright structure.
Clamshell: A bucket with two hinged halves that scoops material by closing together like a clam.
Crane: A mobile machine used for lifting and moving heavy objects, without a bucket.
Crawler crane: A crane with a rotating structure and tracks for moving around a permanent location, such as a power plant.
Digging line: The cable that pulls the bucket on an excavator into the ground. Also known as a “crowd” in a dipper shovel, a “drag” in a pull shovel, and a “dragline” or “closing line” in a clamshell.
Dozer: Short for "bulldozer" or "shovel dozer."
Dozer shovel: A tractor with a front-mounted bucket that can be used for pushing, digging, and loading trucks.
Dragline: A revolving excavator with a bucket suspended by cables that pulls dirt towards itself.
Drop hammer: A pile driver that lifts a heavy weight and then drops it to drive a pile into the ground.
Grader: A machine with a long, adjustable blade in the middle that can be angled to push to either side.
Half-track: A powerful truck with crawler tracks on the back for traction and wheels in the front for steering.
Hydraulic dredge: A machine that uses a pump to suck up a mixture of water and soil and pumps it through pipes onto land.
Industrial tractor: A wheeled tractor with an engine over 20 horsepower, used for various tasks in construction and maintenance. Examples of tasks include mowing lawns, digging holes, and transporting materials.
Jib: An extension that attaches to the end of a crane boom to increase its length and reach. The jib can be straight or angled.
Jib boom: An extension hinged from the upper end of a crane boom for added length.
Live boom: A shovel arm that can be raised and lowered continuously, without stopping the digging cycle.
Load ratings: The maximum weight a crane can safely lift, as specified by the manufacturer.
Mobile job crane: A small hydraulic crane mounted on a truck, with a telescoping boom that can be extended and retracted in two speeds and locked at different angles. Typically used for lifting light loads in workshops and on construction sites.
Power take-off: A part of an engine or transmission where a shaft to power other equipment may be attached.
Sandblaster: A machine that uses a pressurized stream of sand or grit to clean or clear surfaces.
Scarifier: An attachment used to loosen the top layer of a surface, such as a road. Scarifiers can be mounted on graders, rollers, or other machines.
Scraper: A machine used for digging up soil, transporting it over short distances, and then leveling it out. It has a cutting blade, a bowl for carrying dirt, an apron that opens to dump the dirt, and a mechanism to push the dirt out of the bowl.
Shovel dozer: A bulldozer with a front-mounted bucket that can be used for pushing, digging and truck loading.
Stripping shovel: A large excavator with a long arm and digging attachment that allows it to reach far and pile up excavated material high.
Tilting dozer: A bulldozer with a blade that can be angled up or down to cut at different depths on either side.
Tractor: A powerful vehicle used for pulling trailers and operation attachments or other equipment. Tractors may have tracks for better traction on rough terrain, or wheels for easier movement on roads.
Truck Crane: A crane mounted on a truck chassis. It has a rotating upper degment with an engine, controls, and a long boom for lifting and moving lighter loads. The truck itself also provides mobility.
Viscosity: This is the measure of how easily a liquid flows. Liquids with a high viscosity flow slowly and resist movement, while materials with a lower viscosity flow more freely. In construction, different viscosities of oil are used to lubricate machinery parts properly. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) created a rating system to categorize these oil viscosities. You can visit The Difference Between AW-32 and AW-46 Hydraulic Oil to learn more.
Winch: A device that uses a rope or cable to pull or lift heavy objects.
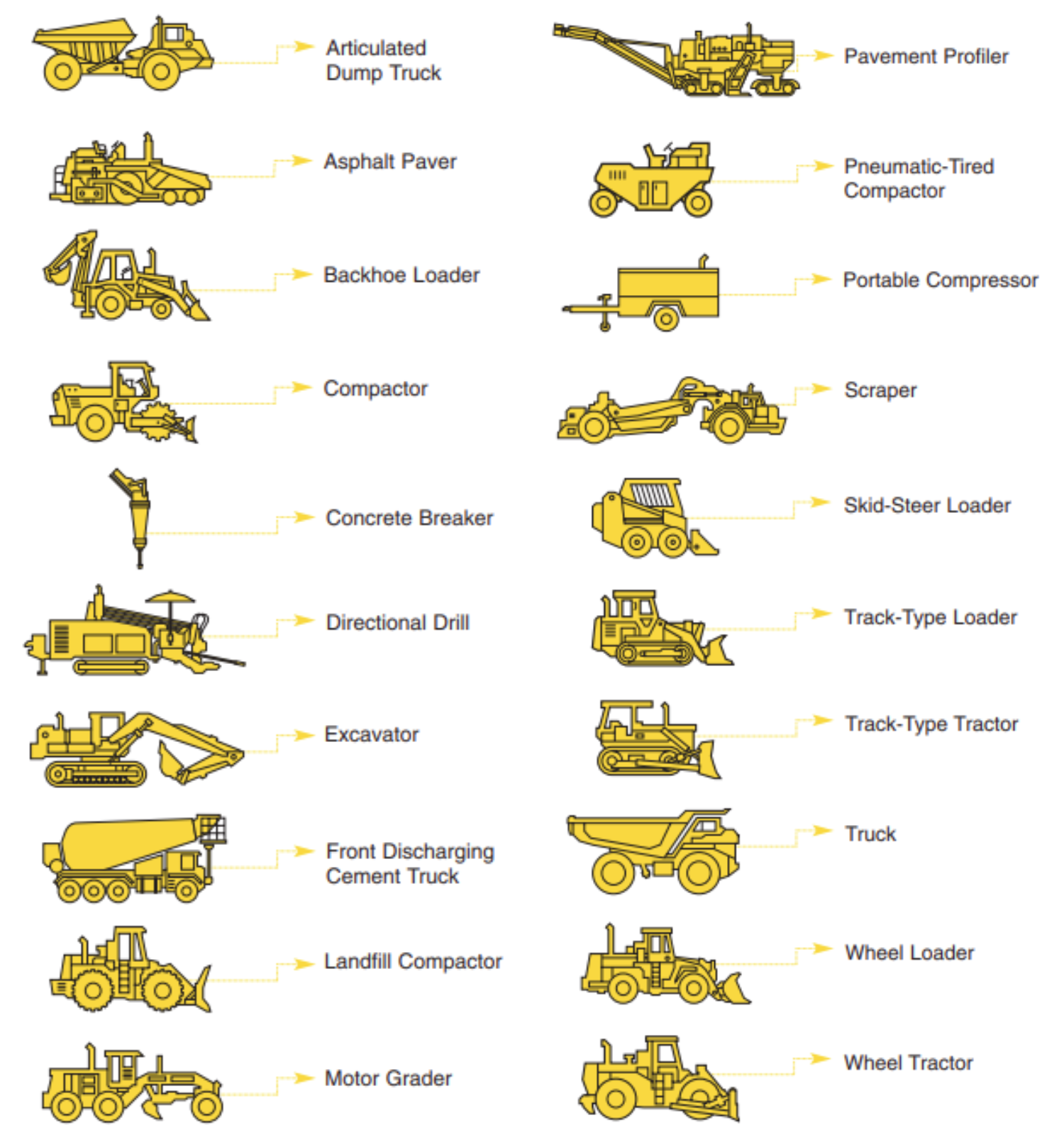
Glossary of Equipment

Additional Resources for the Construction Industry
Construction & Mobile Equipment from Triad Technologies