Don't Get Screwed Over: Metric vs. BSP Threads

In the world of fittings and fasteners, thread type plays a pivotal role in ensuring a secure and reliable connection between components. However, with so many thread types available, choosing the right fit can be confusing. Metric and BSP are two thread types that are often confused due to their shared origin in Britain and similar application. This guide will help you identify the differences between these thread types and determine which is most suitable for your application.
Metric Threads
Metric threads are the standard end fittings used by the International System of Units (SI). These threads are known for being uniform, precise, and reliable under various pressures. When purchasing end fittings and fasteners, you can identify a metric thread by its designation, which typically starts with an 'M', followed by the diameter (in mm) and then the pitch (distance between threads). For example, an M10x1.5 thread indicates a metric fitting with a thread diameter of 10 mm and a pitch of 1.5 mm. Larger pitch threads are more robust and can be assembled more quickly while tighter pitch threads may take longer to assemble but offer better load distribution. Metric threads are commonplace for industrial and mechanical applications in countries that use the metric system, or for equipment manufactured in these countries. Their popularity stems from the simplicity of the metric system and its near-global acceptance.
BSP Threads
BSP threads, short for British Standard Pipe threads, are specialized for sealing systems that convey fluids. They are primarily used in Europe and Commonwealth countries for plumbing, hydraulics, and pneumatic systems. There are two main types of BSP threads:
BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel): These threads run parallel, meaning the diameter remains constant along the length of the thread. A tight seal is achieved using gaskets or O-rings. These are most often found in mechanical joints.
BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper): Unlike BSPP, BSPT threads are tapered, beginning with a smaller width and gradually increasing in diameter as you move towards the main body of the fitting. This taper creates a tighter seal which is better suited for fluid systems.
Similarities and Differences Between Metric and BSP Threads
While both metric and BSP threads serve the purpose of connecting components, some key distinctions set them apart:
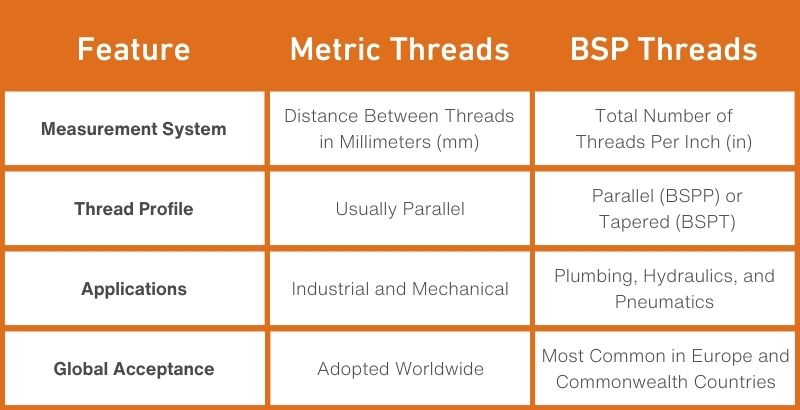

It is important to note that metric and BSP threads are not interchangeable. Attempting to connect a metric component to a BSP threaded part (or vice versa) can lead to an improper seal, which can result in leaks, contamination, and safety hazards. To ensure a proper fit, it is important that you carefully select components with compatible thread types or use the appropriate adapters.
Choosing the Right Thread
Selecting the appropriate thread type hinges on several factors:
Existing Components: When dealing with existing parts with a specific thread type, it's best to selecting components with matching threads. This helps to ensure compatibility and a secure connection. If you aren’t sure what thread type you are using, consult an expert. Sometimes adapters may be necessary to connect parts with different thread types.
Application: When designing a new solution, consider how each type of thread is most commonly used. Metric threads are preferred for general-purpose mechanical applications, while BSP threads are more suitable for fluid transfer systems.
Geography: It is important to note that both of these thread types are more common in Europe than the United States. When working in regions where the metric system is dominant, metric threads are the natural choice. BSP threads might be more prevalent in areas with a history of British standards. American equipment often avoids these thread types all together in favor of NPT threads.
Understanding the distinctions between metric and BSP threads is crucial for selecting the appropriate fittings and ensuring secure connections for your equipment. If you need help with your fitting thread selection, visit your local Triad Technologies ParkerStore. Our experts have the tools to measure and identify threads and ensure you have a tight seal every time. You can also sign up to attend Triad’s Metric Thread ID Training to learn to use thread gauges, calipers, and thread profiles to identify your threads and make your own informed fitting selections.